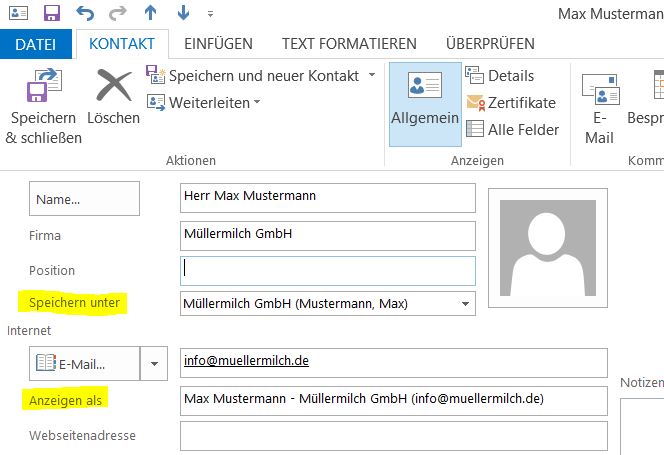
Die Outlook Adresslisten funktionieren am besten, wenn die Datensätze (Kontakte) im gleichem Syntax abgespeichert werden.
Hierbei kann es z.B. Sinnvoll sein, wenn ein der Syntax für das Feld „Speichern unter“ und „anzeigen als“ wie in Abbildung global vorbelegt wird.
Um dies für den eigenen PC oder für einen Terminalserver festzulegen gibt es Makros, welche über Outlook die Registrie des Systems anpassen, so das der Syntax vorbelegt wird.
Das Makro für „Speichern unter“ :
Public Sub ChangeFileAs()
Dim objOL As Outlook.Application
Dim objNS As Outlook.NameSpace
Dim objContact As Outlook.ContactItem
Dim objItems As Outlook.Items
Dim objContactsFolder As Outlook.MAPIFolder
Dim obj As Object
Dim strFileAs As String
Dim myRegKey As String
Dim myValue As String
Dim myFileAs As String
Dim myAnswer As Integer
On Error Resume Next
' get registry key to work with
' change the Outlook version # to match your version
myRegKey = "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Office\15.0\Outlook\Contact\FileAsOrder"
If myRegKey = "" Then Exit Sub
'check if key exists
If RegKeyExists(myRegKey) = True Then
'key exists, read it
myValue = RegKeyRead(myRegKey)
If myValue = 14870 Then myFileAs = "Company"
If myValue = 32791 Then myFileAs = "Last, First"
If myValue = 32792 Then myFileAs = "Company (Last, First)"
If myValue = 32793 Then myFileAs = "Last, First (Company)"
If myValue = 32823 Then myFileAs = "First Last"
'display result and ask if it should be changed
myAnswer = MsgBox("The registry value for the key """ & _
myRegKey & """is """ & myFileAs & vbCrLf & _
"Do you want to change it?", vbYesNo)
Else
'key doesn't exist, ask if it should be created
myAnswer = MsgBox("The registry key """ & myRegKey & _
""" could not be found." & vbCr & vbCr & _
"Do you want to create it?", vbYesNo)
End If
If myAnswer = vbYes Then
'ask for new registry key value
myValue = InputBox("Please enter new value: " & vbCrLf & _
"14870 = Company" & vbCrLf & _
"32791 = Last, First" & vbCrLf & _
"32792 = Company (Last, First)" & vbCrLf & _
"32793 = Last, First (Company)" & vbCrLf & _
"32823 = First Last", myRegKey, myValue)
If myValue <> "" Then
RegKeySave myRegKey, myValue
MsgBox "Registry key saved."
End If
Else
End If
' now that we've got the value of the default setting,
' we use it to set the value so all contacts are the same
Set objOL = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set objNS = objOL.GetNamespace("MAPI")
Set objContactsFolder = objNS.GetDefaultFolder(olFolderContacts)
Set objItems = objContactsFolder.Items
For Each obj In objItems
'Test for contact and not distribution list
If obj.Class = olContact Then
Set objContact = obj
With objContact
If myValue = 14870 Then strFileAs = .CompanyName '"Company"
If myValue = 32791 Then strFileAs = .LastNameAndFirstName '"Last, First"
If myValue = 32792 Then strFileAs = .CompanyAndFullName '"Company (Last, First)"
If myValue = 32793 Then strFileAs = .FullNameAndCompany '"Last, First (Company)"
If myValue = 32823 Then strFileAs = .FullName '"First Last"
.FileAs = strFileAs
.Save
End With
End If
Err.Clear
Next
Set objOL = Nothing
Set objNS = Nothing
Set obj = Nothing
Set objContact = Nothing
Set objItems = Nothing
Set objContactsFolder = Nothing
End Sub
'reads the value for the registry key i_RegKey
'if the key cannot be found, the return value is ""
Function RegKeyRead(i_RegKey As String) As String
Dim myWS As Object
On Error Resume Next
'access Windows scripting
Set myWS = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
'read key from registry
RegKeyRead = myWS.RegRead(i_RegKey)
End Function
'sets the registry key i_RegKey to the
'value i_Value with type i_Type
'if i_Type is omitted, the value will be saved as string
'if i_RegKey wasn't found, a new registry key will be created
Sub RegKeySave(i_RegKey As String, _
i_Value As String, _
Optional i_Type As String = "REG_DWORD")
Dim myWS As Object
'access Windows scripting
Set myWS = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
'write registry key
myWS.RegWrite i_RegKey, i_Value, i_Type
End Sub
'returns True if the registry key i_RegKey was found
'and False if not
Function RegKeyExists(i_RegKey As String) As Boolean
Dim myWS As Object
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
'access Windows scripting
Set myWS = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
'try to read the registry key
myWS.RegRead i_RegKey
'key was found
RegKeyExists = True
Exit Function
ErrorHandler:
'key was not found
RegKeyExists = False
End Function
Quelle 2017-03-08: https://www.slipstick.com/developer/bulk-change-fileas-format-contacts-default/
Das Makro für „anzeigen als“ :
Public Sub ChangeEmailDisplayName()
Dim objOL As Outlook.Application
Dim objNS As Outlook.NameSpace
Dim objContact As Outlook.ContactItem
Dim objItems As Outlook.Items
Dim objContactsFolder As Outlook.MAPIFolder
Dim obj As Object
Dim strFirstName As String
Dim strLastName As String
Dim strFileAs As String
On Error Resume Next
Set objOL = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set objNS = objOL.GetNamespace("MAPI")
Set objContactsFolder = objNS.GetDefaultFolder(olFolderContacts)
Set objItems = objContactsFolder.Items
For Each obj In objItems
'Test for contact and not distribution list
If obj.Class = olContact Then
Set objContact = obj
With objContact
If .Email1Address <>"" Then
' Uncomment the strFileAs line for the desired format
' Add the email address to any string using
' the following code:
' & " (" & .Email1Address & ")"
'Firstname Lastname (email address) format
' strFileAs = .FullName & " (" & .Email1Address & ")"
'Lastname, Firstname format
strFileAs = .LastNameAndFirstName
'Company name (email address) format
' strFileAs = .CompanyName & " (" & .Email1Address & ")"
'Comapany Firstname Lastname (email address) format
'the display name will have a leading space if
'the contact doesn't have a company name
'strFileAs = .CompanyName & " " & .FullName & " (" & .Email1Address & ")"
'File As format
'Does not support Company (Fullname) format.
'Only Company name is used in the display name
'strFileAs = .FileAs
.Email1DisplayName= strFileAs
.Save
End If
End With
End If
Err.Clear
Next
Set objOL = Nothing
Set objNS = Nothing
Set obj = Nothing
Set objContact = Nothing
Set objItems = Nothing
Set objContactsFolder = Nothing
End Sub
Quelle 2017-03-08: https://www.slipstick.com/outlook/contacts/bulk-change-outlook-contacts-email-display-name-format/
Ich habe beide Makro erfolgreich anwenden können.
Viel Spaß und vergesst nicht das Backup davor!!!